- Solar energy blog
- COVID-19: How is it affecting the solar energy industry?
COVID-19: How is it affecting the solar energy industry?


Laura Rodríguez
Territory Manager Oceania & Nordics
Laura is a renewable and software industry sales professional, currently working at RatedPower as Territory Manager Oceania & Nordics. With a background in International Business and International Trade, Laura previously worked in the business strategy area in various companies as well as as a market analyst for the Government of Spain in Australia.

Content
What are the effects of coronavirus in the energy industry now
Worldwide efforts to prevent the expansion of coronavirus have had a significant impact on the energy markets. The changes in the energy demand have affected the gas, oil, coal, and electricity markets as well as the renewable energy forecasts, project viability, and climate programs of many countries.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), energy demand worldwide could drop approximately 6%, which would be equivalent to India’s total annual consumption.
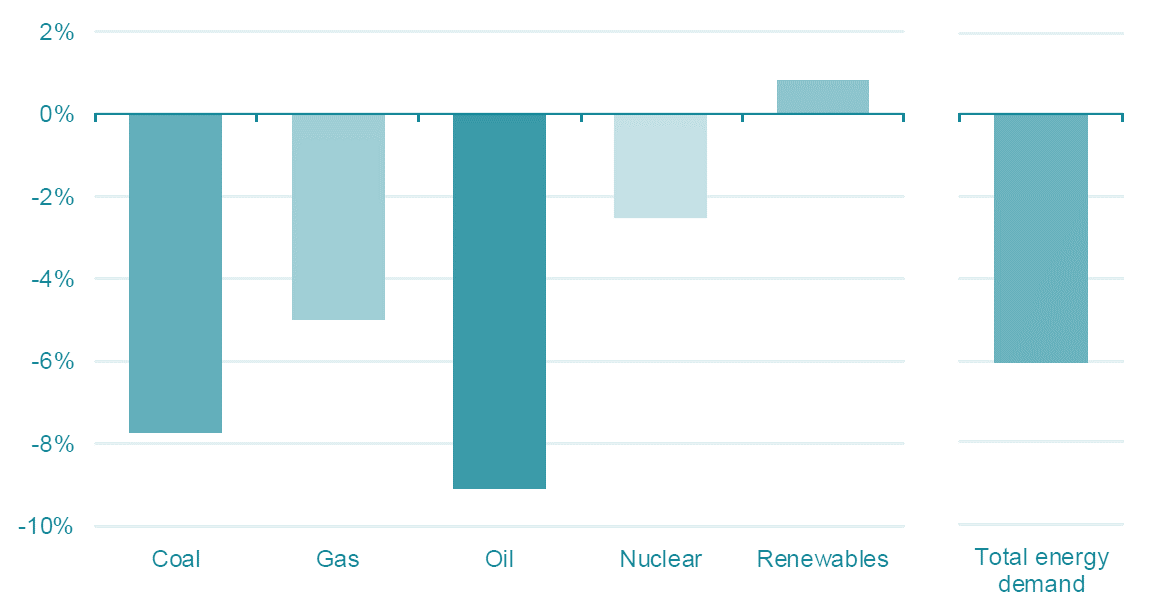
Projected change in primary energy demand by fuel in 2020 relative to 2019 (Source IEA)
Stepping into a Post-COVID Economy: How Renewable Energy and Photovoltaics Will Play an Essential Role in its Recovery. Download eBook for free.
The oil market has experienced one of the biggest impacts with Brent crude prices dropping from $60 to almost $20, the lowest price per barrel in the last 15 years according to Aleasoft and the US oil market Intermediate dropping into negative values. Meanwhile, coal demand is expected to drop by 8% this year and natural gas by 5%.
On a positive note, according to the United Nations, lockdowns and an economic deceleration will cut down emissions by 6% in 2020. According to the IEA, this percentage could increase to an 8%. However, both organisations agree on the importance of government support and policies to maintain the focus on the climate emergency and keep the emissions low. This is important because, in spite of these records, CO2 concentration has kept increasing with respect to 2019.
In terms of the structure of energy generation during the pandemic, some countries such as Spain, one of the most affected by Covid-19, have experienced a growth in photovoltaic generation reaching 6.8% of national production in April in comparison to 4.7% when observed from January to April 2020. Additionally, 47.9% was produced from renewable energies (a 5% increase of the value from January to April).
Observing other countries' electricity trends, we can observe a clear trend throughout the lockdown period. Reduction of coal and gas sources and an increase in renewables.
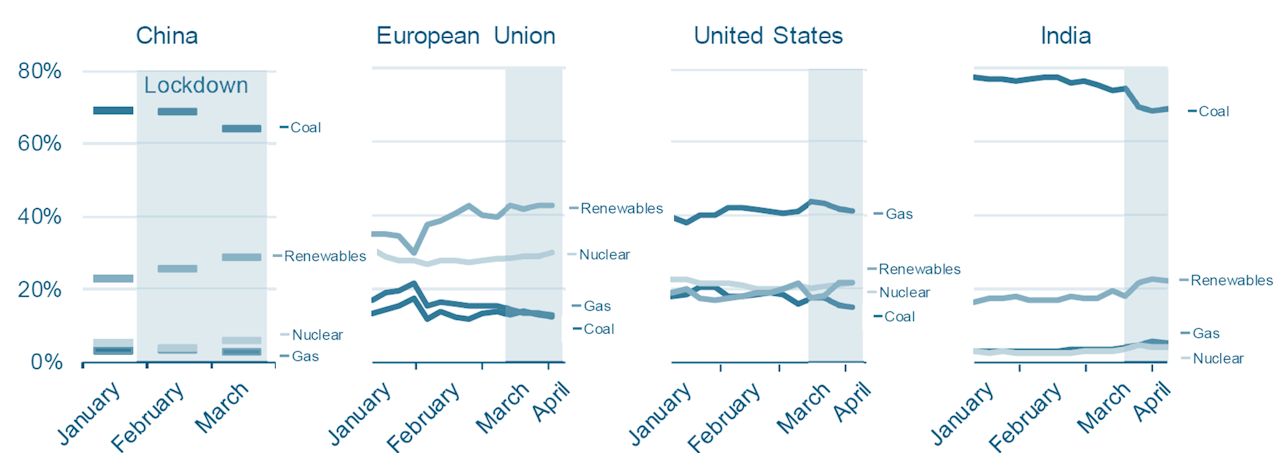
Electricity mix by region in 2020 Source(IEA)
Government incentives towards a green energy transition after Coronavirus
There are several movements that support a green transition as a recovery tool after the crisis.
One of them is the European Alliance, with a Green Initiative supported by 180 business and political leaders, NGOs, group experts, and EU labor unions that support the need to rethink the prosperity model associated with the post-Covid-19 economic recovery.
On a webinar about the new solar sector scenario after the crisis, experts from the solar industry such as Longi, APPA association, Galp, and Power Electronics agreed that renewable energies could and should be the motor of the economic recovery.
These ideas can be reinforced by the actions already taken by several governments worldwide.
Israel’s plan to recover from Covid-19 crisis includes 2 GW of new solar. In the United States, the number of 100+ MW solar projects is rapidly increasing and they believe that if there is one solar segment that can weather a pandemic, it’s utility-scale photovoltaics.
In Spain, the National Energy and Climate Plan “Plan Nacional Integrado de Energía y Clima (PNIEC)” estimates an investment of 241,400 million euros (80% private and 20% public and European financed) between 2021 y 2030 for the impulse of the renewable transition, efficiency measures and network and electrification improvements within the new European Green Deal.
Social resilience and economic viability towards the same goal: Energy transition
2020 was expected to be the turning point towards climate and sustainable development as seen in the last COP25 meeting in Madrid. Under the slogan “Time for Action”, global energy leaders presented their opinions and forecasts toward a greener future.
This determination has endured even under the worst, unimaginable circumstances with the outbreak of Covid-19.
As an example, market leaders reports such as Iberdrola, Repsol, or Lightsource BP show that they have reinforced their objectives. An unprecedented investment of 10,000 million euros was announced by Iberdrola to reactivate the economy with renewable projects and smart grids. Repsol, on the other hand, has announced its first solar farm right in the middle of the worst oil price crisis in the last 20 years. Others such as Lightsource, Galp, or module manufacturers state that despite the global temporary slow down, their projects, manufacturing rates, and construction pipelines are still going strong.

In the end, the key takeaway that we have seen through many reviews and webinars of solar experts is that if a project was viable before the crisis, it will still be viable in the long-run.
The key to success according to experts
Adopt new digital technologies such as for solar software design or for asset management.
Analyze well the viability of future projects.
Invest in innovation such as batteries or bifacial modules.
According to the International Energy Agency, renewables will be ‘the only energy source likely to experience demand growth for the rest of 2020’.
Latest stories
Related posts
Market analysis
A look at the largest-scale solar projects across the UK
Find out more about how the UK is developing substantial solar power projects, including the Queequeg Renewables Solar PV Park and the Botley West Solar Farm.
Updated 24 FEB, 26

Market analysis
Battery Storage in Africa: From Backup to Backbone
See why Africa is prioritizing off-grid battery storage that operates independently, as 50% of its population doesn’t have access to a stable power supply.
Updated 19 FEB, 26

Market analysis
How Italy is repowering aging solar into assets
Discover more about how Italy is breathing new life into its aging solar plants, boosting output, and driving toward the country’s 2030 climate goals
Updated 27 JAN, 26

- RatedPower
- Solar energy blog
- COVID-19: How is it affecting the solar energy industry?
 Watch a demo
Watch a demo

