How to pick the best solar software for your team
A buyer’s guide to solar design and engineering software
Utility-scale solar plants will play an essential role in enabling the transition to green as countries around the world move to reduce their carbon emissions and address climate change.
The digitalization of solar energy systems is key to scalability for utility-scale projects to manage resources effectively. The advanced data and analysis capabilities solar software provide enable project developers and operators to take advantage of economies of scale and maximize their return on investment.

What is solar software?
Solar photovoltaic (PV) software is a design tool that assists solar development, construction and engineering companies to plan their PV projects for optimal energy efficiency, from the design phase through to construction and operation.
Software packages can help organizations to design layouts, optimize the configurations, track the cost of materials and installation, create energy consumption estimates, and plan the integration of energy storage systems.
Companies can then use the designs in sales proposals and follow up with leads faster. The modeling functionality saves companies time and money with accurate remote site assessment that allows them to assess a project site without leaving the office.
When it comes to utility-scale installations, developers, utilities, IPP, and other solar engineering firms face particular challenges as projects increase in size.
THE ROLE OF SOLAR ENERGY SOFTWARE AS A LCOE REDUCER
How does it help?
The sharp decline in the cost of solar equipment over the past decade has made it more viable to develop projects with large installed capacities of hundreds of megawatts.
But with bigger project portfolios, those working in the space need to manage and interpret growing volumes of data to ensure they keep on top of their operations —keeping LCOE low from the very begining of its PV project pipeline, as proposed by Patrick MacLeamy back in 2004.
Solar software systems help industry stakeholders streamline their repetitive tasks by automating the design process and allowing them to manage project requirements on a single dashboard.
For systems that are operational, project operators can identify assets that may be underperforming and gain visibility into maintenance requirements, allowing them to reduce downtime and the impact on revenue.
Segmenting the solar software landscape
There are a variety of options available for solar software packages. For clarity sake, we’ll categorize them based on two variables.
The table below will help you navigate PV software alternatives which are a fit for both — the market segment you, as a professional serve, and the lifecycle stage your team specializes in.
Scientific literature usually split PV plant lifecycle in three stages: Project, operation and end-of-life phases. This guide will focus in the project stage, where you can find the following areas:
- By lifecycle stageThe buyer also needs a specific set of tools depending on where they sit in the solar project lifecycle, from development through to the operation and maintenance and end-of-life phases.
- By PV market segmentThe requirements of a prospective solar software buyer will vary dramatically depending on the size of their projects. In this regard, we’ll find PV software for residential, commercial and industrial (C&I), or utility scale.
Solar design software by use case

Site selection
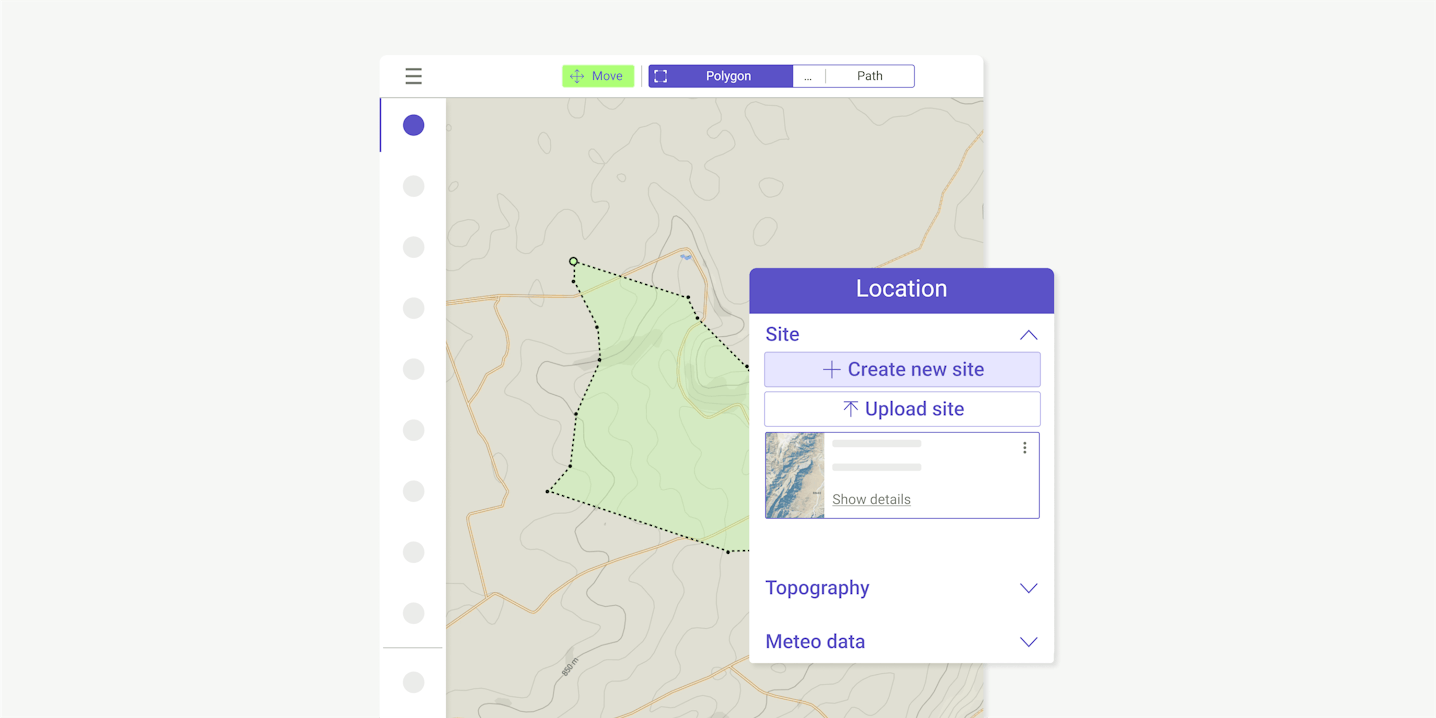
Accessing and review resource, grid and geospatial data, such as topography or meteo data streams.

Pre-planning
Concept, feasibility study, financing and funding, permits & licensing.

Energy yield estimates
Financial modelling, CAPEX, OPEX and energy output.

Design & engineering
Specification, outline & detailed design.

Construction
Procurement, logistics, site preparation & environment mitigation, mounting structures & assembly subsystems, certification & commissioning, connection to power grid.
Solar design software by market segment
Residential
<10kW per rooftop
Helping businesses design the layout for rooftop PV solar panels. Usually it includes sales proposal modules.
Commercial & Industrial
<1MW per facility
Used by contractors to design and optimize PV installations on commercial and industrial (C&I) buildings.
Utility-Scale
>1MW per plant
Set of solutions for large scale designers and engineers.
Site selection
Pre-planning
Energy estimates
Design & engineering
Construction
Solar design alternatives reviews
Helioscope
Read on to learn how RatedPower stacks against Helioscope.

Terabase
Read on to learn how RatedPower stacks against Terabase.
PVcase
Read on to learn how RatedPower stacks against PVcase.
PVsyst
Read on to learn how RatedPower stacks against PVsyst.

Prospect sites efficiently
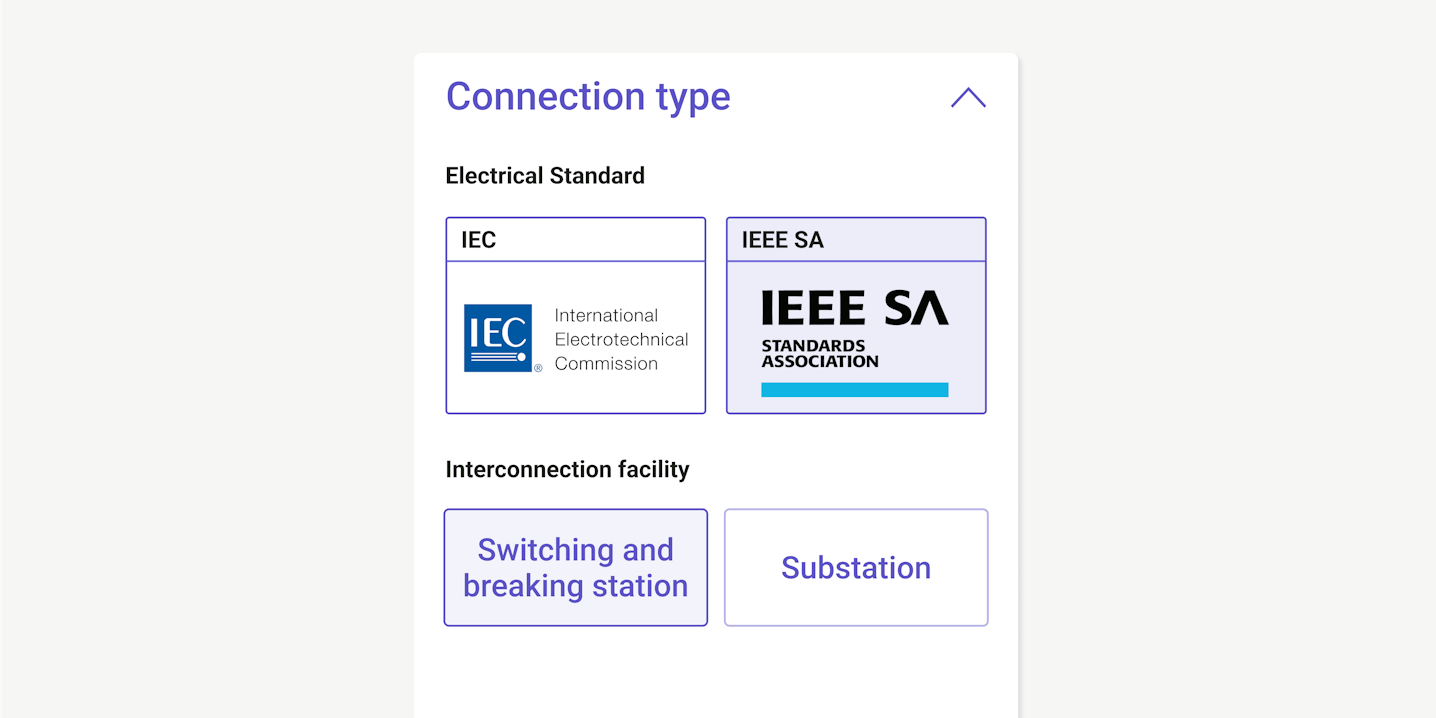
Find the best electrical configuration
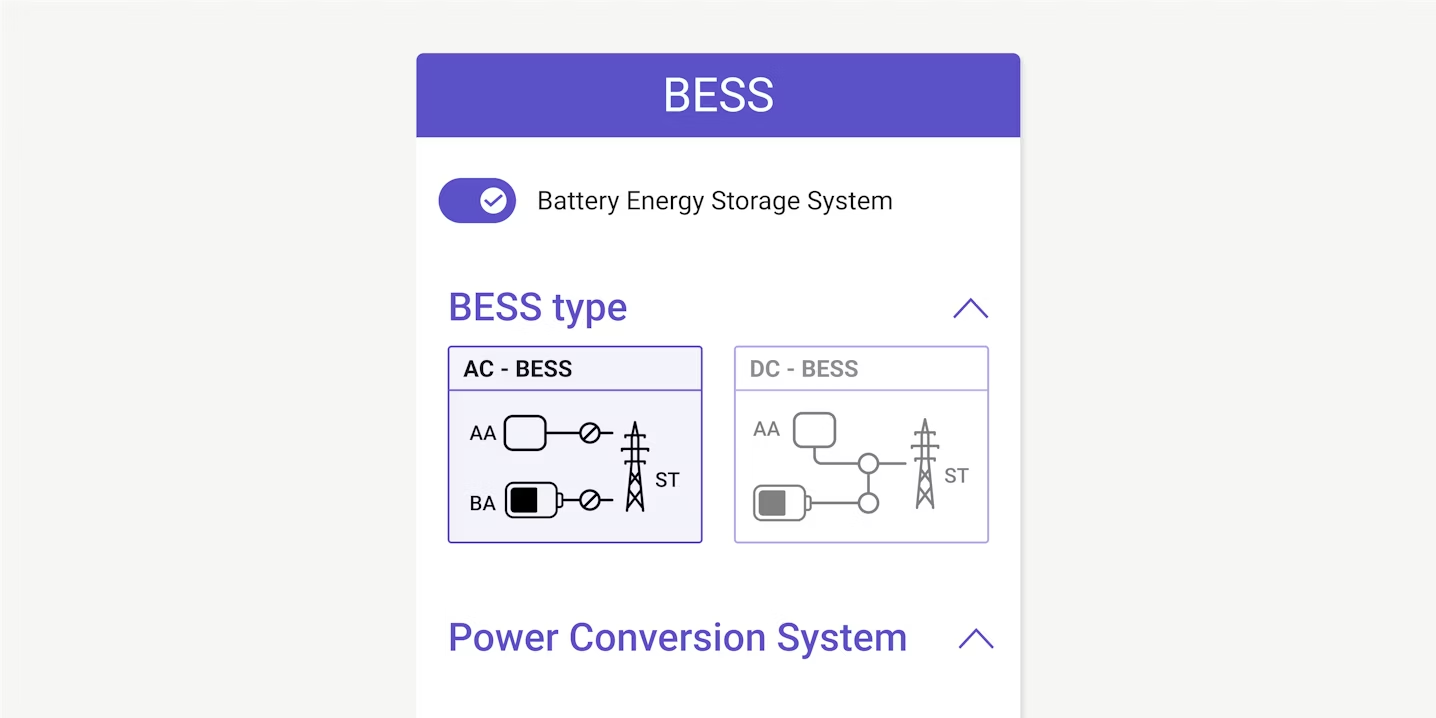
Hybridize your plant with BESS
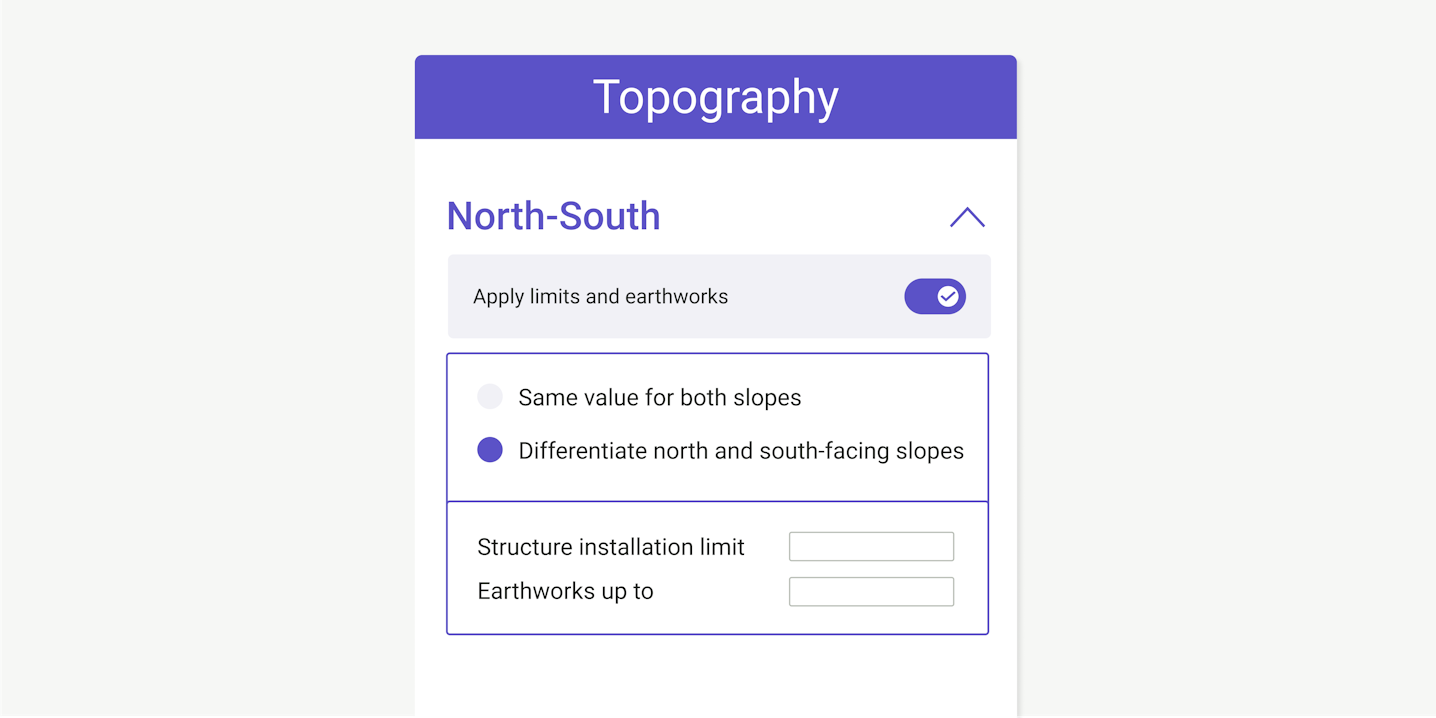
Perform cut-and-fill cost-benefit analyses
Optimize land use
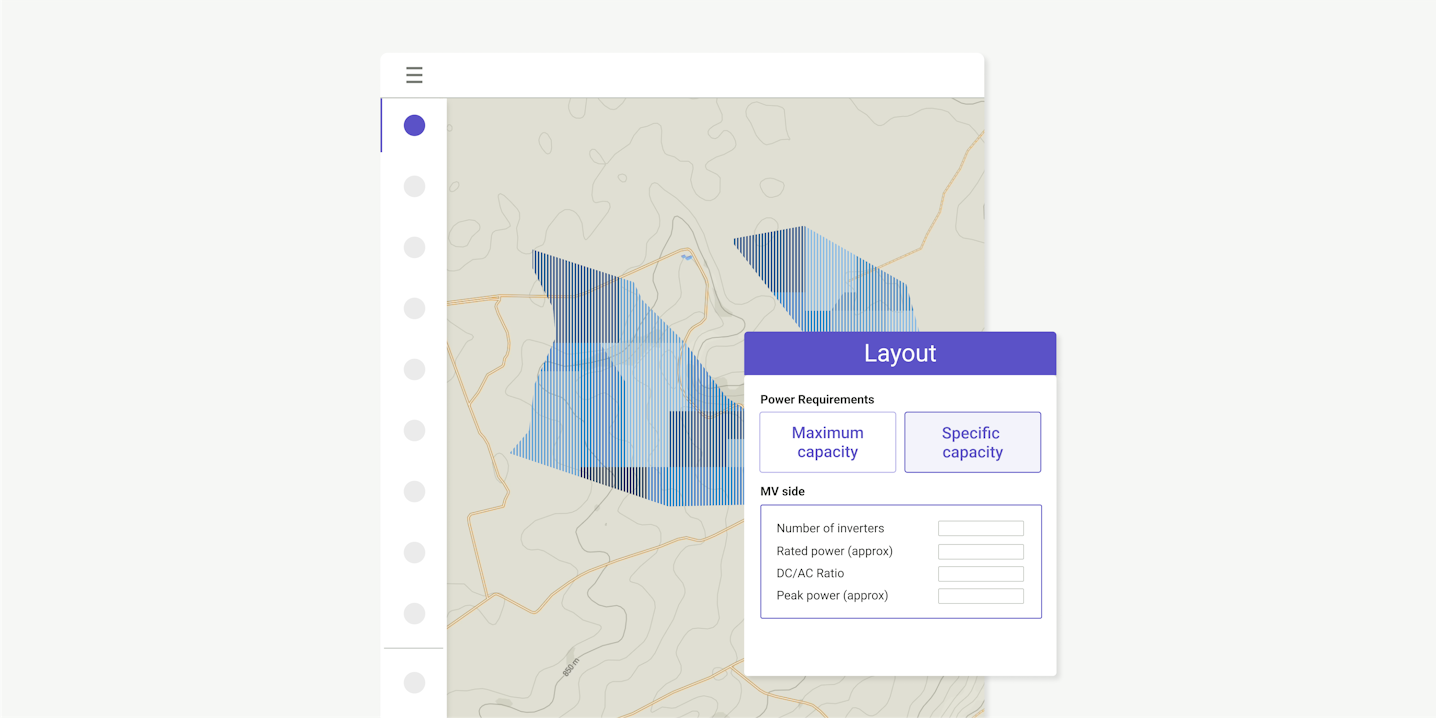
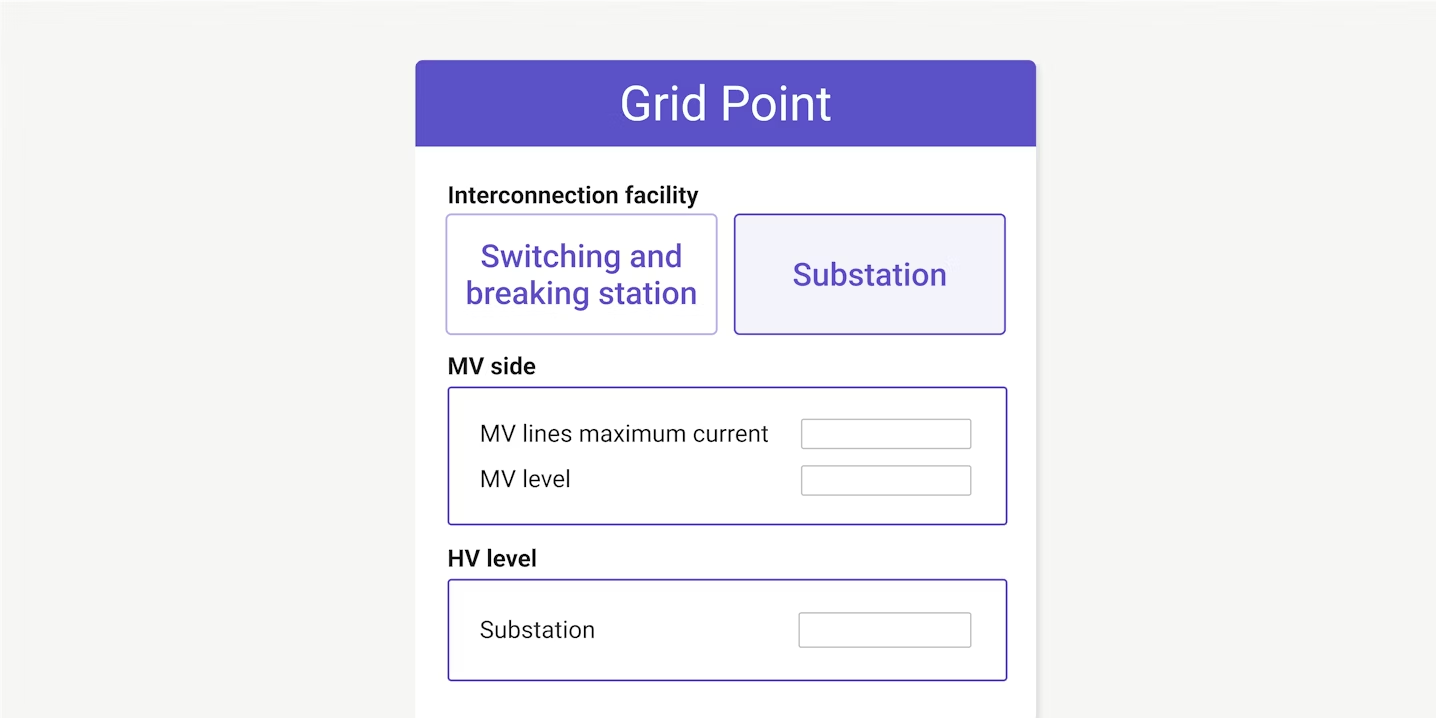
Simplify your interconnection process
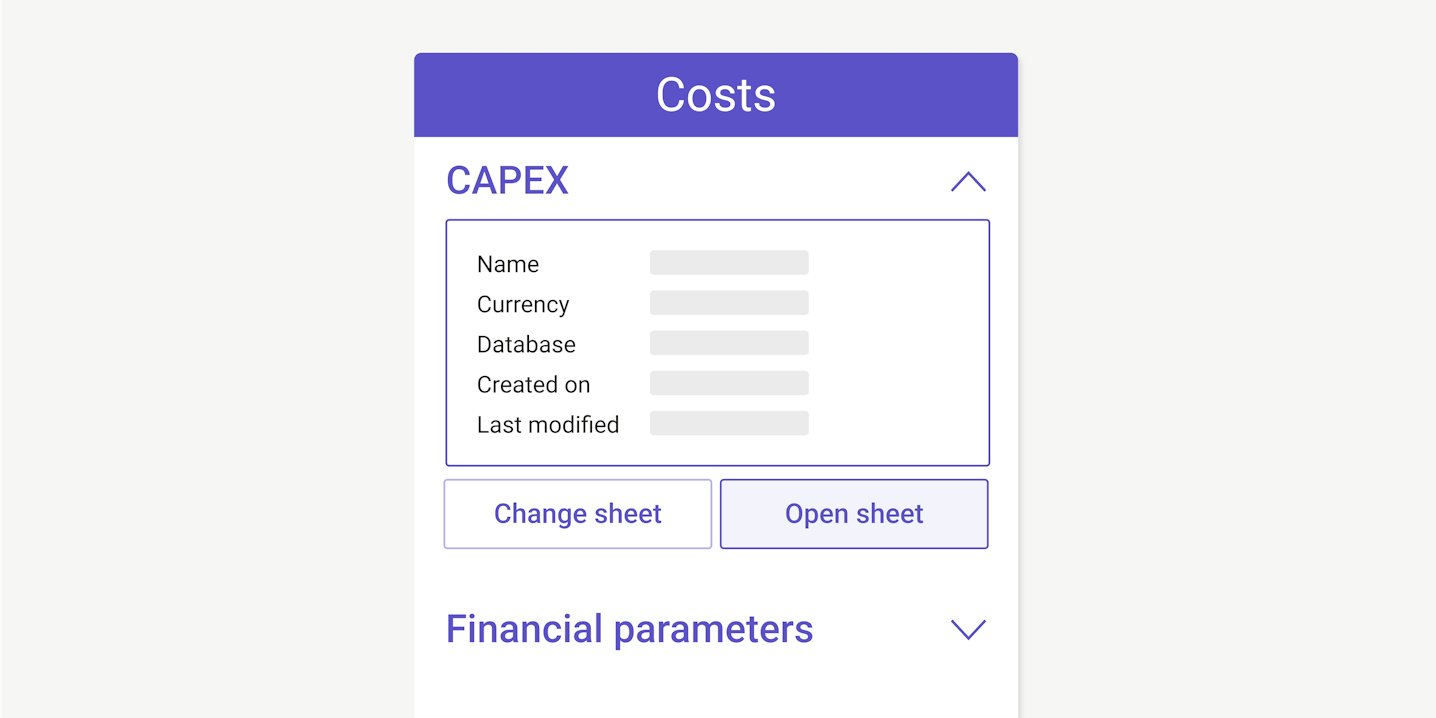
Quote projects with accurate BoM, CAPEX, and LCOE
Determine project capacity and energy yield
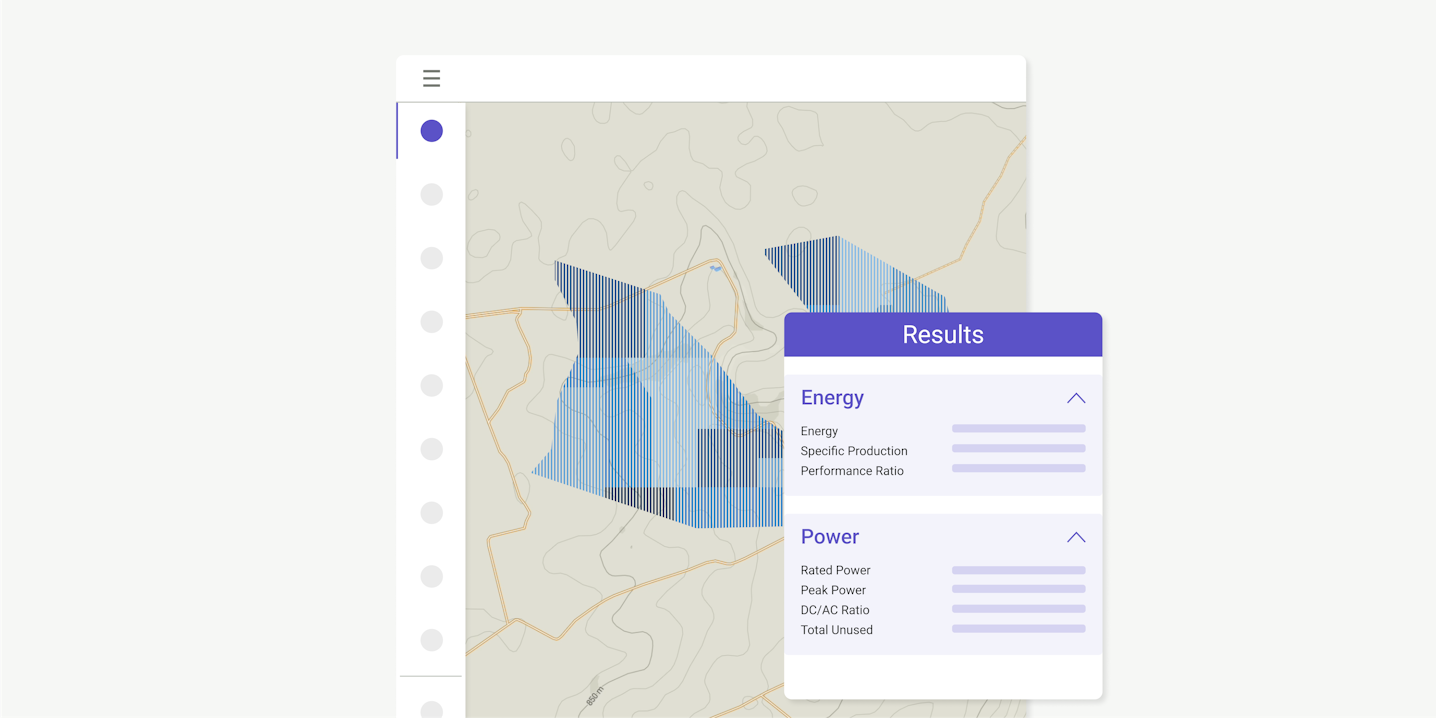
Find the optimal layout with GCR, tilt and DC/AC ratio iterations
Utility-scale solar design and engineering software stacks
What stacks are out there?
Regardless of the type of business, there are some common features you need to be able to work on a solar project — and technically document them so it can be used down the project pipeline:
- Layout and equipment definition.
- Electrical and civil setup.
- Energy yield forecasting.
- Financial analysis.
- Permits and administrative documentation.
- Grid access and interconnection.
- Compatibility of input file types among your tech stack and results shareability.
Benefits of solar project management software
Why do solar engineers and designs prefer solar software?
There are clear advantages for solar industry professionals in using end-to-end specialized software for utility-scale solar plants instead of CAD software.
-
Solar engineers and designers can quickly compile drawings and documentation for large-scale projects, automating complex calculations and reducing the risk of manual errors.
-
They can factor every component in the system into their designs and make use of advanced modeling capabilities to create the most accurate plans.
-
PV teams can replace a suite of tools with a single application. Ultimately, that empowers them to increase their efficiency, and deliver more on-time projects.
Old school PV software stacks
A basic software stack may be composed of generic desktop applications that are not specific to the solar industry, like Microsoft Excel and AutoCAD.
These programs are cheaper to procure but they require manual development work to run complex calculations.
These technology packages are the most flexible. They can be used for many different projects and produce customized results.
However, they do not offer any solar-related features, such as shading analysis and component layout.
Most companies will use AutoCAD to some extent, which is a general CAD software package with design automation.
Companies that need to do only basic analysis will make limited use of CAD software, while companies doing more advanced engineering work will be heavy users of more advanced CAD tools, such as AutoCAD Civil.
Some software examples from this category include:
- MS Office suite
- Google Earth and other mapping tools (QGIS)
CAD software with sunny vitamines
Adding plugins that are tailored to solar projects allows companies to introduce a level of automation to their desktop applications. Many use PVsyst or their alternatives. PVsyst is the totem of photovoltaic energy yield estimation.
Commonly found in many solar engineering teams. It's very customizable but, as a trade-off, it lacks automation. It's a fantastic tool for energy yield calculation —it has been used for almost 30 years— . However, getting results with it requires extensive experience and engineering hours.
Some companies also use AutoCAD plugins to speed up the time it takes to design the layout, such as PVcase or PVCAD.
These solutions require less manual work, but because they are still within the AutoCAD ecosystem, the documentation production capabilities or the computer hardware requirements for simulation utility-scale PV plants are limited.
Whether companies use specialized plugins for performance and financial analysis will depend on where they sit in the project pipeline. Companies that work on the later stages of a project, such as detailed engineering work, may not need to do any performance analysis as the project is already financed at that stage.
Some solar software examples from this category include:
- PVsyst, or its alternatives
- AutoCAD PV plugins, such as PVcase, Helios3D or PVCAD.
Specialized end-to-end PV software
For a technology solution tailored specifically to those working on solar projects, companies can use specialized PV project planning tools, like RatedPower or Helioscope, to supplement their traditional tech stack tools.
The cost of establishing these stacks can be higher, but they also have greater throughput. Some GIS tools for solar also fit in this category, such as Anderson Optimization and Terabase.
They offer a higher degree of automation than the more basic systems. Companies can develop engineering designs and off-taker proposals from a single app, integrating information from a range of sources —from meteorological or topography to equipment library— .
Specialized solar software applications include a range of features specifically targeted at PV project design at utility-scale.
They offer energy projections, module and inverter configuration, terrain shading modeling, transmission and interconnection data, financial analysis, and simulation settings.
Some examples on this solar software category are:
- RatedPower, PlantPredict, Terabase, HST for utility-scale PV
- Helioscope, PVSol for commercial, industrial and small utility-scale projects
- GIS prospecting solutions such as Anderson
- Optimization for utility-scale projects
- Aurora Solar for rooftop solar installations
Fully custom in-house software
Some companies develop their own internal tools to produce detailed solar project designs up to their corporate specifications and standards.
Large companies are more likely to allocate resources to devise tailored software stacks that meet their specific requirements for project development.
The total cost of ownership is higher as developing and maintaining software requires a huge amount of IT investment.
For the utility-scale segment
While some apps are versatile enough to serve several segments, this guide focuses its analysis on the solar software available for the utility-scale segment at the project stage.
Key PV system design software features to watch out
To design a solar energy system, users need a PV plant layout tool that incorporates all the components to visualize the installation of modules and structures. It should place structures in the correct location and take into account physical restrictions like bodies of water, trees, and slopes.
The topographical analysis allows users to study the suitability of different parts of the site based on their preferred criteria. An advanced tool will modify the terrain to simulate the execution of earthworks.
The layout tool can generate georeferenced drawings of the different elements of the layout, including:
- General layout
- Topographical and terrain slope analysis
- Structures profiles
- LV and MV cables
- Modules
- Power stations and other plant buildings
- Roads
- Fences
Users need a tool that designs the layout of the electrical equipment, placing all the different power stations, combiner boxes and cables in the project. Ideally, the tool will also size all the electrical elements such as cables, protection devices and transformers.
Based on the electrical equipment defined by the user, the software will design the blocks that best fit the configuration for each inverter, string box, or DC bus in the optimal position. It will then set out the cables and trenches based on the positions of the electrical equipment.
An algorithm will find the shortest path to minimize cable length, and size the cables based on the local standard.
Users need a tool that allows them to simulate how much energy the PV installation will produce. The calculations can also give users a detailed sheet of results and take into account 3D modeling.
Some solar software solutions provide site design optimization tools but do not include financial reporting. This means engineering teams still need to use separate systems to compile their proposals. This takes more time than an end-to-end solution and has an impact on how many projects the team can work on, at any one time.
Some common examples of this flexibility options are:
- Adjusting the position of layout components in the PV plant, such as internal roads, structures, or power stations
- Edit electrical system design and size, such as allowed cable sections
- Change internal parameters of the energy simulation, such as the heat constants or the soiling losses
The software should provide login authentication to prevent access from unauthorized users. For example, RatedPower requires users to authenticate through AWS Cognito, using OAuth2 or federated authentication.
Cloud-based applications are also easy to set up for users needing access with remote installation and login, rather than desktop software applications that need to be installed on each device.
What’s more, subscription-based services offer regular automatic updates, without having to upgrade to the latest version of a desktop software application.
- RatedPower
- Solar software guide