What is energy yield and why is it relevant when designing solar plants?




Félix Pérez
Principal Software Engineer
Felix is a PV engineer and software developer, specializing in the development of calculation models and algorithms. After working in an engineering firm, he joined RatedPower to lead the development of the energy and topography calculation models of pvDesign, with a focus on building robust engineering software. Felix is enthusiastic about all disciplines of engineering, and enjoys discussing the more nuanced aspects of both. He is also very passionate about research, which has been a constant through his career in RatedPower.

Read on to learn what energy yield is and how is it used in the design of solar PV plants.
What is energy yield?
Definition of Energy Yield: Energy yield is the energy produced by a renewable energy system, such as a solar PV installation. It accounts for external factors that reduce output in solar systems, like shading and accumulated dirt on panels.
Energy yield differs from power ratings, which indicate the maximum potential energy generation under ideal lab test conditions. Instead, energy yield aims to provide a practical, realistic estimate of how much energy can be produced by a system in its operating environment.
Why is energy yield important?
Accurately estimating and maximizing energy yield allows solar developers and asset owners to predict how much electricity a solar system can generate, thus shaping financial modeling and profitability analyses. Accurate yield forecasts can reduce solar financing costs by providing educated estimates around returns.
Energy yield projections influence system design choices to optimize peak production at the site based on environmental factors. Tracking energy yield during solar operations helps diagnose underperformance issues and identify opportunities to improve output through maintenance and operational changes.
Some additional things to know about energy yield:
Experts calculate it through solar modeling software that uses the system's specifications and historical weather data for the location.
Two parameters which help analyze the system efficiency are performance ratio and specific production.
Optimizing designs and operations to maximize energy yield is vital to lowering the levelized cost of solar electricity.
Energy Yield Methodology
If you would like to understand how the energy yield calculation model works on the RatedPower platform please check out the methodology at the following link.

Design utility-scale solar at lightning speed
Maximizing energy yield: a breakdown of pvDesign vs PVsyst
Listen back to this webinar to uncover the solar software comparison between pvDesign and PVsyst with a special emphasis on energy yield analysis.
Latest stories
Related glossary posts
Technology and engineering
What is a solar substation and how to customize yours with RatedPower software
Updated 5 MAY, 25

Technology and engineering
What is a solar combiner box and why is it used in photovoltaic designs?
Updated 25 MAR, 25

Technology and engineering
What are the benefits of a Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) for solar plants
Updated 25 MAR, 25

Related posts
Technology and engineering
Innovation in renewable energy: Developments expected in 2025
We look at the 10 biggest renewable industry developments that are making a green future possible, including perovskite solar cells, green hydrogen, and more.
Updated 18 MAR, 25

Technology and engineering
The era of standalone energy yield software is ending
Updated 19 APR, 22

Technology and engineering
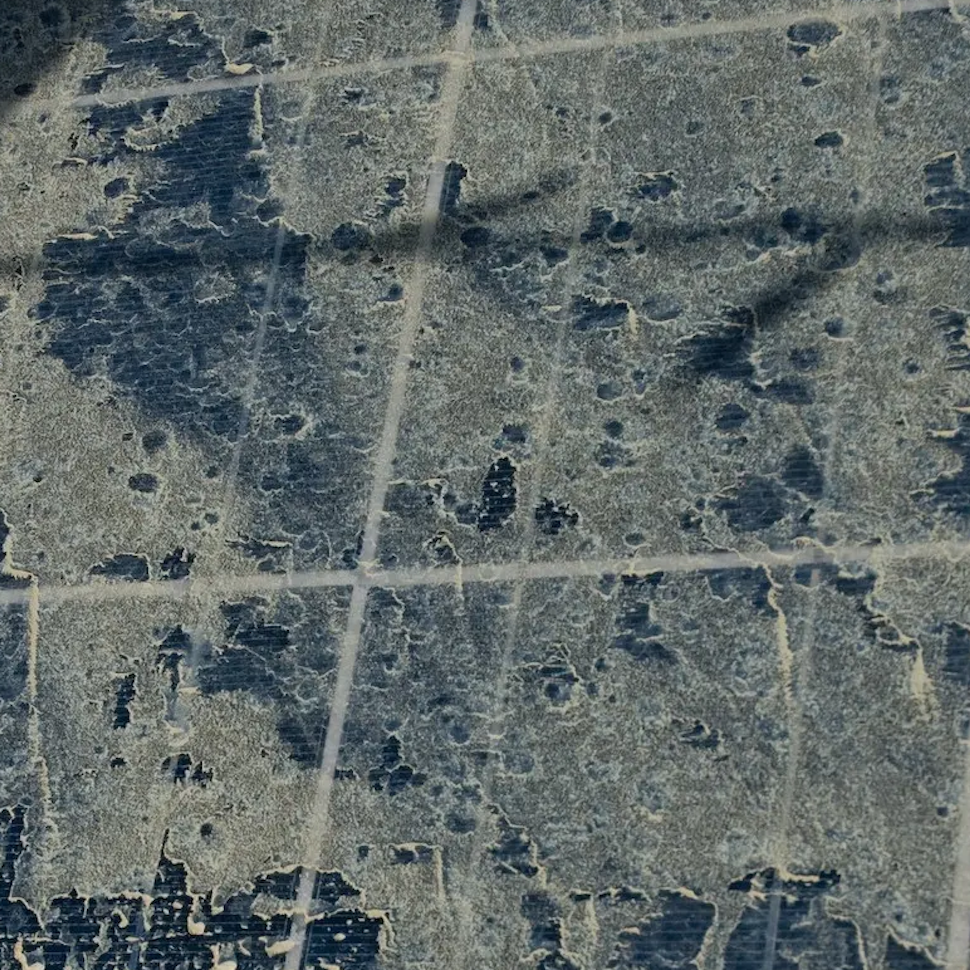
How to battle soiling losses with RatedPower
How do soiling losses affect the output from a solar energy system and how can RatedPower help to account for them in a PV project?
Updated 22 FEB, 22

- RatedPower
- Glossary
- E
- Energy yield



