How is an IV Curve used to maximize solar output?


Jeremy Vickerman
Senior Content Manager
Senior Content Marketing Manager at RatedPower with extensive experience in content strategy, production, and communications. Over a decade of expertise spanning marketing, recruitment consulting, and public relations across the UK and Spain, with a strong track record in driving brand visibility and audience engagement.


Enio Gjoni
Sr. Product Owner
Enio Gjoni is an electrical engineer with expertise in power system analysis and studies. Having dedicated 5 years contributing in the "Control Room of the Future" for transmission utilities, by being part of the implementation team of cutting-edge SCADA/EMS/AGC systems, he has joined RatedPower as a Senior Product Owner in the Interconnection team, committed in bringing to the users a top-tier software solution for solar power studies.

Read on to learn what an IV curve is and how it's used in solar plants to ensure panels optimize their output.
What is a Solar IV Curve?
Solar IV Curve definition: A Solar IV Curve is a graphical representation of how a specific solar cell operates. It is used to visualize the relationship between current and voltage under the varying irradiance and temperature conditions. The intensity of the solar radiation, referred to as insolation, that hits the cell controls the current (I), while the increase in the temperature of the solar cell reduces its voltage (V).
The Solar IV Curve plays a crucial part in how solar PV cells are developed and allows us to understand a solar cell device, its ability to convert solar energy, and its efficiency.
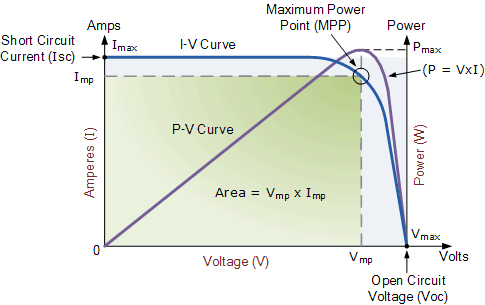
Source: Alternative Energy Tutorials
Why are Solar IV Curves important?
For a solar PV plant to offer the maximum return on investment, each panel needs to be calibrated to absorb and convert solar energy at the highest efficiency level possible. Using a Solar IV Curve gives engineers the information they need to calibrate panels and achieve peak efficiency.
The Solar IV Curve can also help identify issues with panels. Modules are tested during the manufacturing process under standard conditions (STC) which is an irradiance of 1000W/m2, a temperature of 25C and an air mass of 1.5.
When a solar PV system is performing as expected, the IV curve should follow the normal profile. If there are any issues, or the IV curve shows actual power output does not match the predicted value, analysis of the IV curve will help identify the root cause of the issue.
Solar IV curves also play a large part in estimating the actual performance of a solar PV plant. Panels will almost always underperform once installed. A string of solar cells will only provide as much current as the worst-performing cell in the string and the coating of a solar cell will also reduce output. These factors mean that modeling a solar IV curve after installation is essential for determining the actual performance of your plant.
Our software has everything you could possibly need to build your PV project with confidence and reduce risk. Check out our demo, or get in touch with us for more information.

Design utility-scale solar at lightning speed
eBook: Minimize your shading losses with RatedPower
Download this eBook to examine what shading losses are, the different types of shading, and how you can minimize the shading losses of your next PV installation.

Latest stories
Related glossary posts
Technology and engineering
How solar zenith and azimuth impact panel efficiency
Updated 8 SEP, 25

Technology and engineering
Albedo and Solar Power: What You Should Know
Updated 8 SEP, 25

Technology and engineering
What is a solar substation and how to customize yours with RatedPower software
Updated 5 MAY, 25

Related posts
Technology and engineering
Outsmarting congestion: How efficient solar design helps navigate Nordic grid limits
Learn how Nordic operators and solar developers are adjusting to tighter grid conditions and how policy and design decisions are keeping projects on track.
Updated 16 DEC, 25

Technology and engineering
The rise of ultra-thin perovskite solar cells
Learn about Japan’s $1.5B initiative to commercialize ultra-thin, flexible perovskite solar cells and how it could transform the solar landscape globally.
Updated 30 SEP, 25

Technology and engineering
The green hydrogen boom in LatAm
Latin America is emerging as a green hydrogen leader. Learn how LatAm countries are leveraging solar and wind power to drive green hydrogen production.
Updated 22 JUL, 25

- RatedPower
- Glossary
- I
- IV curve
 Watch a demo
Watch a demo


