- Solar energy blog
- Renewable industry developments and innovations to look out for in 2025
Renewable industry developments and innovations to look out for in 2025
We look at the 10 biggest renewable industry developments that are making a green future possible, including perovskite solar cells, green hydrogen, and more.



Can renewable energy finally outpace coal and redefine how the world powers itself? With renewables already fueling over 30% of global electricity in 2024, that future isn’t far off. By 2025, renewable electricity is expected to surpass coal as the world’s leading energy source, marking a turning point in the fight against climate change.
But this transformation isn’t limited to electricity grids. Green hydrogen is carving a niche in heavy industry and transport, while bioenergy and advanced technologies are reshaping homes and businesses. With policy backing and rapid innovation, renewables are transforming global energy. Here’s what’s driving the change.
Top 10 key innovations in renewable energy
1. Perovskite solar cells
Perovskite solar cells are transforming solar power with dramatic efficiency gains and affordability. These cells have advanced from 3% efficiency in 2009 to over 25% today, rivaling traditional silicon panels. Tandem solar cells that combine perovskite and silicon layers further boost efficiency to above 30%, surpassing the limits of silicon alone.
Despite their promise, stability remains a challenge. Exposure to moisture, oxygen, or heat degrades perovskites, but solutions such as protective encapsulation layers and improved materials are under development. Scaling production is another focus, with researchers exploring cost-effective and reliable manufacturing techniques.
Perovskites’ lightweight and flexible nature enables integration into windows, rooftops, and portable devices. As advancements continue, these cells could outpace silicon in performance and affordability, revolutionizing the solar industry.

2. Green hydrogen
Green hydrogen is emerging as a zero-carbon fuel for sectors that are difficult to electrify, such as heavy industry and long-haul transportation. Produced through water electrolysis powered by renewable energy, it provides a clean alternative for decarbonizing steel, chemicals, and shipping.
Between 2020 and 2024, green hydrogen projects reached 434 final investment decisions, up from 102 in 2020. Investments grew from $10 billion to $75 billion, while electrolyzer capacity doubled. China leads the push, accounting for 60% of global electrolyzer manufacturing.
However, high production costs remain a barrier, with green hydrogen costing several times more than fossil fuel alternatives. Developers are addressing water scarcity in arid regions through desalination and wastewater treatment. Technological advancements and supportive policies could fuel production to reach 49 million tons annually by 2030.
3. Advanced energy storage solutions
Energy storage is important for balancing renewable energy supply and demand. Solid-state, flow, and thermal batteries surpass lithium-ion with higher energy density, longer life, and greater safety.
Solid-state batteries are gaining traction in electric vehicles and grid-scale storage. In contrast, flow batteries using liquid electrolytes are preferred for large-scale projects due to their reliability and long discharge times. Thermal storage systems, such as molten salt, enhance solar energy use by storing heat for nighttime electricity generation.
The global energy storage market is projected to grow at a compound annual rate of 9.5%, reaching $31.72 billion by 2031 from $12.80 billion in 2023. With declining costs and new technologies like sodium-ion batteries, energy storage will continue to enable renewable energy expansion.
4. Advances in bifacial solar panels
Bifacial solar panels are designed to capture sunlight from both sides, increasing efficiency and energy output. In environments with reflective surfaces like snow, sand, or water, these panels can generate up to 30% more electricity than conventional panels.
Bifacial panels capture more energy, allowing fewer panels to meet the same demands — a clear advantage for large solar farms. Recent advancements in solar tracking systems that follow the sun’s movement further improve their performance.
As production scales, bifacial panels' costs are falling, making them increasingly accessible for commercial and residential use. Their ability to deliver higher energy yields with smaller footprints positions them as a necessary technology for maximizing solar energy production.
5. Advances in floating solar farms
Floating solar farms, or “floatovoltaics,” are gaining popularity as a solution to land scarcity. By using water surfaces like reservoirs or lakes, these farms avoid competing with land for agriculture or development. Additionally, the cooling effect of water enhances their efficiency by up to 15%.
Asia leads global adoption, with Japan’s floating farms and China’s 78,000 MW Anhui project providing clean energy for thousands of homes. Covering just 10% of the world’s reservoirs with floating solar panels could produce 20 TW of electricity, 20 times the current global solar capacity.
Challenges such as installation costs, saltwater corrosion, and environmental concerns remain. However, improved standards and government incentives are expected to drive the adoption of this innovative technology.
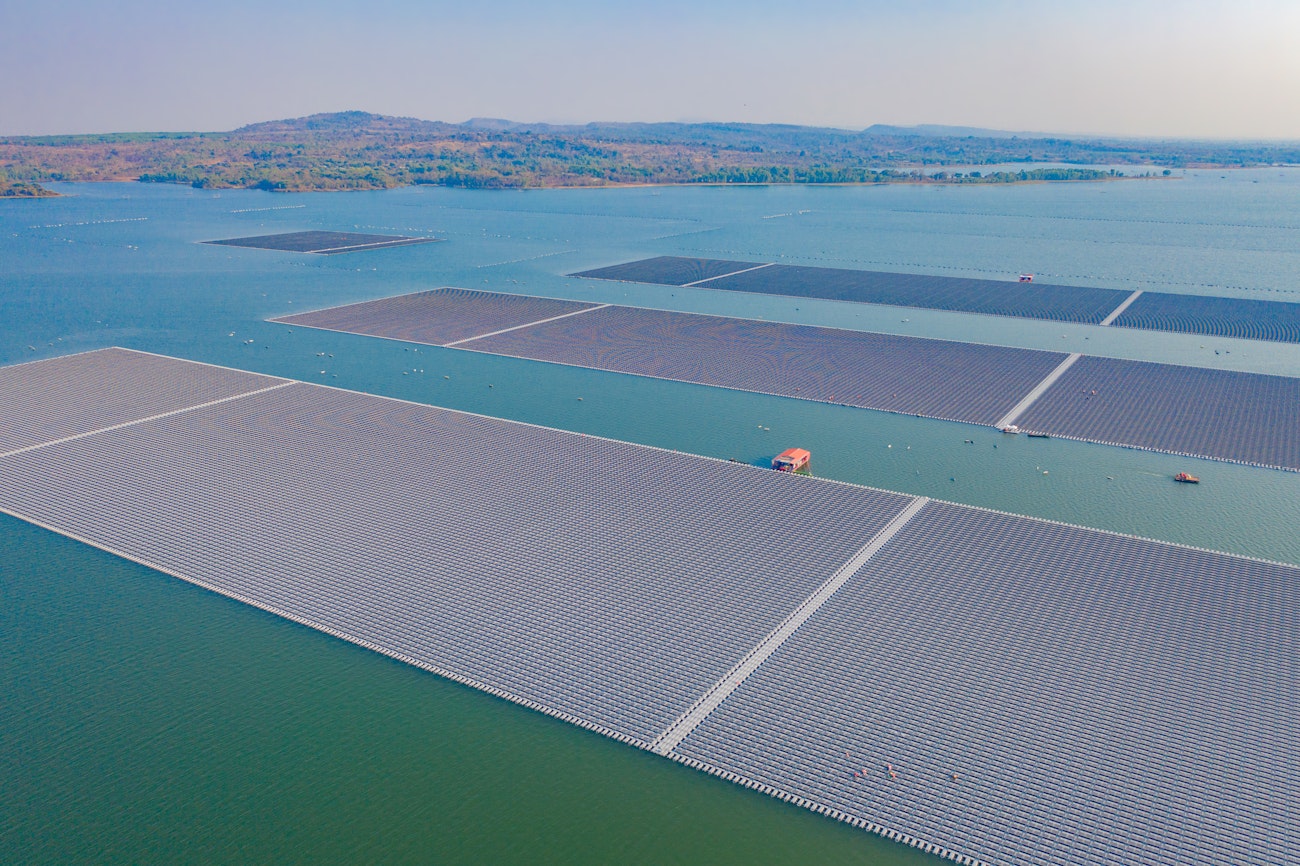

6. Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) Cells
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) store energy from wind and solar, making power available even when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing. They’re key to keeping renewable energy reliable. Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) cells, known for their thermal stability and long lifespans, are becoming a preferred choice for grid storage and electric vehicles.
Newer options like sodium-ion and zinc-based batteries are cheaper and safer than lithium ones, helping solve supply issues and material shortages. The global BESS market saw impressive growth, rising from $5.51 billion in 2023 to $6.99 billion in 2024, and is expected to continue its rapid expansion through 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of 26.8%.
7. AI and digital twin technology in energy systems
Artificial intelligence (AI) and digital twin technologies deliver real-time insights and advanced optimization capabilities. AI enhances grid stability by accurately predicting energy demand and supply, which helps streamline operations and cut costs.
Digital twins, which are virtual replicas of physical energy assets, allow for precise simulations and performance analysis, improving planning and efficiency. Together, these technologies make it easier to integrate renewable energy into the grid while ensuring stability as adoption continues to grow.
8. Wind turbine innovations
Wind turbine advancements are increasing energy output with new designs and materials. Floating turbines enable offshore wind farms in deeper waters, while larger blades capture more energy, even at low wind speeds.
Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs) are better suited for urban environments or regions with variable wind patterns, as they capture wind from any direction. Wooden turbine towers are reducing production costs and emissions compared to steel, making wind energy more sustainable.
These advancements are lowering costs and increasing efficiency, making wind energy a scalable and viable renewable resource.
9. Blockchain in energy management
Blockchain is transforming energy management by enhancing transparency and efficiency. It enables peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing consumers to buy and sell surplus renewable energy directly. Blockchain also ensures traceability for renewable energy certificates, fostering trust and accountability.
Decentralized ledgers improve grid management by tracking energy generation and consumption. The blockchain-powered energy market is expected to grow at a compound annual rate of 71.1% between 2023 and 2030, driven by innovative applications and widespread adoption.
10. Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS)
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) captures CO2 emissions and stores them underground, helping industries lower their carbon output.
The European Union plans to develop 50 million tons of CO2 storage capacity by 2030, while the UK has allocated £20 billion for CCS projects to store 30 million tons annually.
In the US, over $8 billion has been invested in CCS programs through 2026, with projects like Chevron’s Gorgon facility in operation.
Costs and scalability are hurdles, but with government support and a focus on industries like cement and fertilizer, CCS can become viable. It’s not a one-size-fits-all solution, but it’s vital for sectors with limited green options.
Looking to 2025 and beyond
These advancements are transforming renewable energy by boosting efficiency, cutting costs, and enhancing storage and management. As they evolve, they promise to speed up the shift toward a sustainable, carbon-free future.
Latest stories
Related posts
Technology and engineering
Solar Power Technologies that rocked it in 2022
Updated 14 NOV, 22

Technology and engineering
Learn PV substation engineering and design automation with RatedPower
Do you know why and how a solar farm connects to the grid? RatedPower automatically generates the best solution for an interconnection facility and chooses between a switching and breaking station, a line to transformer substation or a single/double busbar substations.
Updated 2 DEC, 21
Market analysis
Breaking down solar farm costs: Free template inside
Updated 27 SEP, 21

- RatedPower
- Solar energy blog
- Renewable industry developments and innovations to look out for in 2025


